Health Information-Seeking Behavior Related to COVID-19: A Literature Review
Health Information-Seeking Behavior
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.52845/currentopinion.v4i1.282Keywords:
health-seeking behavior, COVID-19, vaccination, good health, well-beingAbstract
Introduction: Health information-seeking behavior is an activity carried out to obtain information that originates from a need. This research aims to conduct a literature review regarding health information-seeking behavior related to COVID-19.
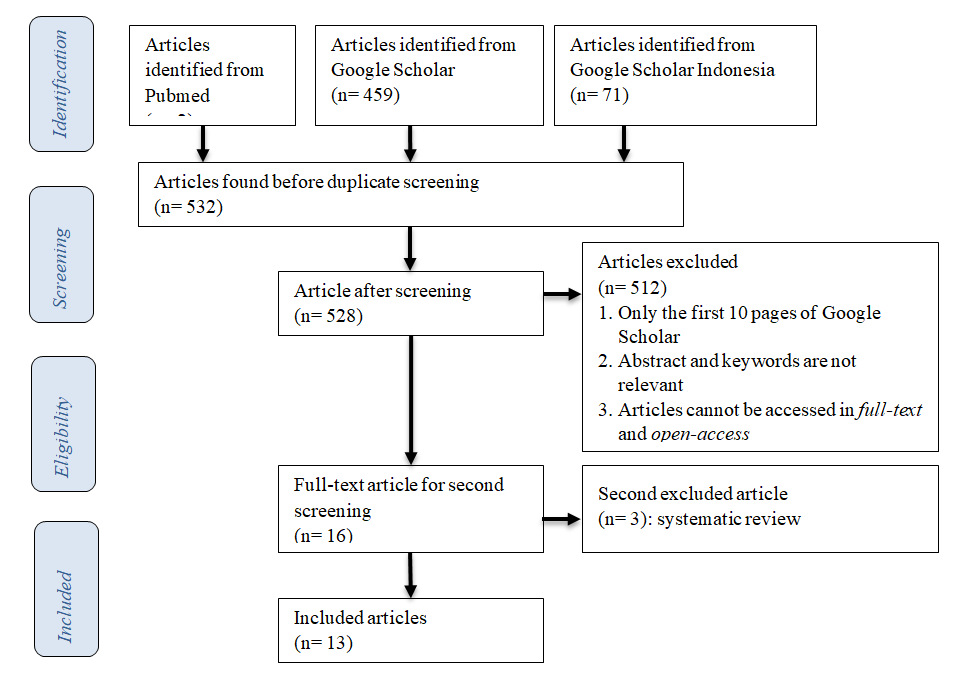
Method: A literature review was conducted from the Pubmed, Google Scholar, and Google Scholar Indonesia digital databases published in English and Indonesian between 2018 and 2023. The author used search terms on Pubmed and Google Scholar "health" AND "information" AND "seeking" AND "behavior" AND "generation Z" AND "COVID-19" AND "vaccination"; while on Google Scholar Indonesia, the author used search terms "perilaku" DAN "pencarian" DAN "informasi" DAN "kesehatan" DAN "generasi Z" DAN "vaksinasi" DAN "COVID-19".
Results: Thirteen studies included in the literature review were published between 2021 and 2023 which 69% used quantitative studies, 23% used qualitative studies, and 8% used a mixed method. All the research designs used were cross-sectional research. Most of the studies (53%) were conducted in Asia, 31% in Europe, 8% in America, and 8% in Africa. Most studies (77%) use test instruments to measure and only 23% conducted narrative interviews.
Discussion: Most studies show that the most frequently used sources of information are social media, television, word of mouth from friends, family, society, radio, health applications or official websites, doctors, or health experts. The types of information most sought after are regarding COVID-19 vaccination, the COVID-19 virus, guidance for self-care during the COVID-19 period, disease prevention and management, and vaccine accessibility.
Conclusions: This literature review found that searching for health information influences people's behavior regarding the decision to vaccinate against COVID-19, so the role of aspects related to processing positive information in the use of the COVID-19 vaccine is important.
Downloads